Hip

Dr. Burns specializes in arthroscopic treatment of the hip. Arthroscopic management of labral tears, femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), hamstring/gluteal injuries, and trochanteric bursitis have seen tremendous advancements over the past decade. We are now able to perform procedures, that previously required large incisions, through a couple of 1 cm incisions. Patients are able to recover from these procedures much quicker and return to sports/activities at a higher rate.

Please see the links below for information on hip anatomy, injuries and surgical treatments. Please also review the patient info tab above to find new patient forms, preoperative instructions, postoperative instructions, and physical therapy guidelines for these procedures.
Hip Anatomy
The hip joint is the largest weight-bearing joint in the human body. It is also referred to as a ball and socket joint and is surrounded by muscles, ligaments and tendons. The thighbone or femur and the pelvis join to form the hip joint.
Any injury or disease of the hip will adversely affect the joint's range of motion and ability to bear weight.
The hip joint is made up of the following:
- Bones and joints
- Ligaments of the joint capsule
- Muscles and tendons
- Nerves and blood vessels that supply the bones and muscles of the hip
Bones and Joints of the Hip
The hip joint is the junction where the hip joins the leg to the trunk of the body. It is comprised of two bones: the thighbone or femur, and the pelvis, which is made up of three bones called ilium, ischium and pubis.
The ball of the hip joint is made by the femoral head while the socket is formed by the acetabulum. The acetabulum is a deep, circular socket formed on the outer edge of the pelvis by the union of three bones: ilium, ischium and pubis. The lower part of the ilium is attached by the pubis while the ischium is considerably behind the pubis. The stability of the hip is provided by the joint capsule or acetabulum and the muscles and ligaments that surround and support the hip joint.
The head of the femur rotates and glides within the acetabulum. A fibrocartilaginous lining called the labrum is attached to the acetabulum and further increases the depth of the socket.
The femur is one of the longest bones in the human body. The upper part of the thighbone consists of the femoral head, femoral neck, and greater and lesser trochanters. The head of the femur joins the pelvis (acetabulum) to form the hip joint. Next to the femoral neck, there are two protrusions known as greater and lesser trochanters which serve as sites of muscle attachment.
Articular cartilage is the thin, tough, flexible and slippery surface lubricated by synovial fluid that covers the weight-bearing bones of the body. It enables smooth movements of the bones and reduces friction.
Ligaments of the Hip Joint
Ligaments are fibrous structures that connect bones to other bones. The hip joint is encircled with ligaments to provide stability to the hip by forming a dense and fibrous structure around the joint capsule. The ligaments adjoining the hip joint include:
- Iliofemoral ligament: This is a Y-shaped ligament that connects the pelvis to the femoral head at the front of the joint. It helps in limiting over-extension of the hip.
- Pubofemoral ligament: This is a triangular shaped ligament that extends between the upper portion of the pubis and the iliofemoral ligament. It attaches the pubis to the femoral head.
- Ischiofemoral ligament: This is a group of strong fibers that arise from the ischium behind the acetabulum and merge with the fibers of the joint capsule.
- Ligamentum teres: This is a small ligament that extends from the tip of the femoral head to the acetabulum. Although it has no role in hip movement, it does have a small artery within that supplies blood to a part of the femoral head.
- Acetabular labrum: The labrum is a fibrous cartilage ring which lines the acetabular socket. It deepens the cavity increasing the stability and strength of the hip joint.
Muscles and Tendons of the Hip Joint
A long tendon called the iliotibial band runs along the femur from the hip to the knee and serves as an attachment site for several hip muscles including the following:
- Gluteals: These are the muscles that form the buttocks. There are three muscles (gluteus minimus, gluteus maximus, and gluteus medius) that attach to the back of the pelvis and insert into the greater trochanter of the femur.
- Adductors: These muscles are in the thighs which help in adduction, the action of pulling the leg back towards the midline.
- Iliopsoas: This muscle is in front of the hip joint and provides flexion. It is a deep muscle that originates from the lower back and pelvis, and extends up to the inside surface of the upper part of the femur.
- Rectus femoris: This is the largest band of muscles located in front of the thigh. They are also called hip flexors.
- Hamstring muscles: These begin at the bottom of the pelvis and run down the back of the thigh. Because they cross the back of the hip joint, they help in extension of the hip by pulling it backwards.
Nerves and Arteries of the Hip Joint
Nerves of the hip transfer signals from the brain to the muscles to aid in hip movement. They also carry the sensory signals such as touch, pain, and temperature back to the brain.
The main nerves in the hip region include the femoral nerve in the front of the femur and the sciatic nerve at the back. The hip is also supplied by a smaller nerve known as the obturator nerve.
In addition to these nerves, there are blood vessels that supply blood to the lower limbs. The femoral artery, one of the largest arteries in the body, arises deep in the pelvis and can be felt in front of the upper thigh.
Hip Movements
All the anatomical parts of the hip work together to enable various movements.Hip movements include flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction, and hip rotation.
Conditions
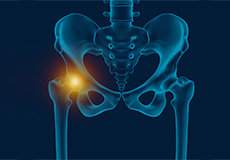
Hip Pain
Hip pain, one of the common symptoms that patients complain of, may not always be felt precisely over the hip joint. Pain may be felt in and around the hip joint and the cause for pain is multifactorial. The exact position of your hip pain suggests the probable cause or underlying condition causing pain.
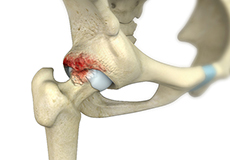
Femoroacetabular Impingement
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is a condition where there is too much friction in the hip joint from bony irregularities causing pain and decreased range of hip motion.
The femoral head and acetabulum rub against each other creating damage and pain to the hip joint.
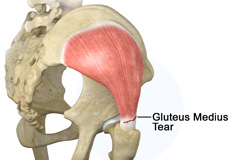
Gluteus Medius Tear
A gluteus medius tear is a condition characterized by severe strain on the gluteus medius muscle that results in partial or complete rupture of the muscle.
The gluteus medius is one of the major muscles of the hip and is essential for movement of the lower body and keeping the pelvis level during ambulation.

Hip Labral Tear
A hip labral tear is an injury to the labrum, the cartilage that surrounds the outside rim of your hip joint socket.
The hip joint is a ball and socket joint in which the head of the femur is the ball and the pelvic acetabulum forms the socket. The labrum helps to deepen the socket and provide stability to the joint. It also acts as a cushion and enables smooth movements of the joint.
Snapping Hip Syndrome
The hip is an important joint that helps us walk, run and jump. The ball-and-socket joint in the hip is formed between the round end of the femur (thighbone) and the cup-shaped socket of the acetabulum (part of the hip bone). Joint stability in the hip region is achieved through the labrum (a strong fibrous cartilage), which covers the acetabulum and seals it, and ligaments (tissue connecting bone to bone) and tendons (tissue connecting muscle to bone) that encase the hip and control the hip movements.
Your surgeon will discuss the best surgical option depending on your condition.
Non-Surgical Treatments

Hip Injections
Hip joint injections involve injecting medicine directly into the hip joint to diagnose the source of pain or treat pain due to conditions such as arthritis, injury or mechanical stress of the hip joint. Hip pain may be experienced in the hip, buttock, leg or low back.

Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy
Our blood consists of a liquid component known as plasma. It also consists of three main solid components which include the red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. Platelets play an important role in forming blood clots. They also consist of special proteins, known as growth factors, which help with our body’s healing process. Platelet-rich plasma or PRP is a high concentration of platelets and plasma.
Surgical Treatment

Hip Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole or minimally invasive surgery, is a procedure in which an arthroscope is inserted into a joint to check for any damage and repair it simultaneously.
An arthroscope is a small, fiber-optic instrument consisting of a lens, light source, and video camera.

FAI Labral Repair
Coming soon

FAI Labral Debridement and Psoas Release
Coming soon

Cam/Pincer Osteoplasty
The hip forms a ball and socket joint. The ball-shaped surface of the femur (thighbone) fits and glides smoothly in a cup-like depression or socket of the acetabulum (hip bone).

Capsular Plication for Instability
Coming soon

Hip Labral Repair
The labrum is a ring of strong fibrocartilaginous tissue lining around the socket of the hip joint. It serves many functions where it acts as shock absorber, lubricates the joint, and distributes the pressure equally. It holds the head of the femur in place and prevents the lateral and vertical movement of the femur head within the joint. It also deepens the acetabular cavity and offers stability against femoral head translation.

Trochanteric Bursectomy
Coming soon

Gluteus Medius Repair
Gluteus medius is one of 3 muscles in the buttocks and is situated on the outer surface of the hip. The function of the gluteus medius is to assist with pelvis stability, hip abduction, along with internal and external rotation of the hip. Tears of the gluteus medius usually occur where the tendon inserts at the greater trochanter, causing lateral hip pain.

Proximal Hamstring Repair
Coming soon

Management of Snapping Hip
Snapping hip syndrome is a condition in which you hear or feel a snapping sound in the hip while swinging your legs, running, walking or while getting up from the chair. Movement of the muscles or tendons over a bony protrusion in the hip region gives rise to the snapping sound, which can occur in the back, front or side of the hip. It is usually painless and harmless, but may be accompanied with pain and weakness in some.